Unerstanding HTML in Angular is the foundation for developing solid and adaptable web applications. Angular is a framework that employs HTML as the foundation in developing robust and dynamic views. In regular HTML, you just write static code, whereas in Angular, HTML interacts with components, data binding, and directives to animate pages.
This combination of HTML and Angular capabilities enables you to manage user input, apply styles to elements, and regulate page behavior without reloading. When you know how HTML functions within Angular, you can develop cleaner, faster, and more maintainable code that makes your apps better to look at and function.
What is HTML in Angular
HTML in Angular is not plain markup. It is enhanced with Angular features like interpolation, property binding, event binding, and directives. These features connect HTML with the component’s logic written in TypeScript.
This means you can create HTML that reacts to changes in your data instantly. For example, if you have a variable title = ‘Hello World’ in your component, writing {{ title }} in your template will automatically show “Hello World” on the screen. If the value of title changes, the text updates without refreshing.
You Will Like : JavaScript | Working with Objects | Angular
HTML Templates and the Component Structure
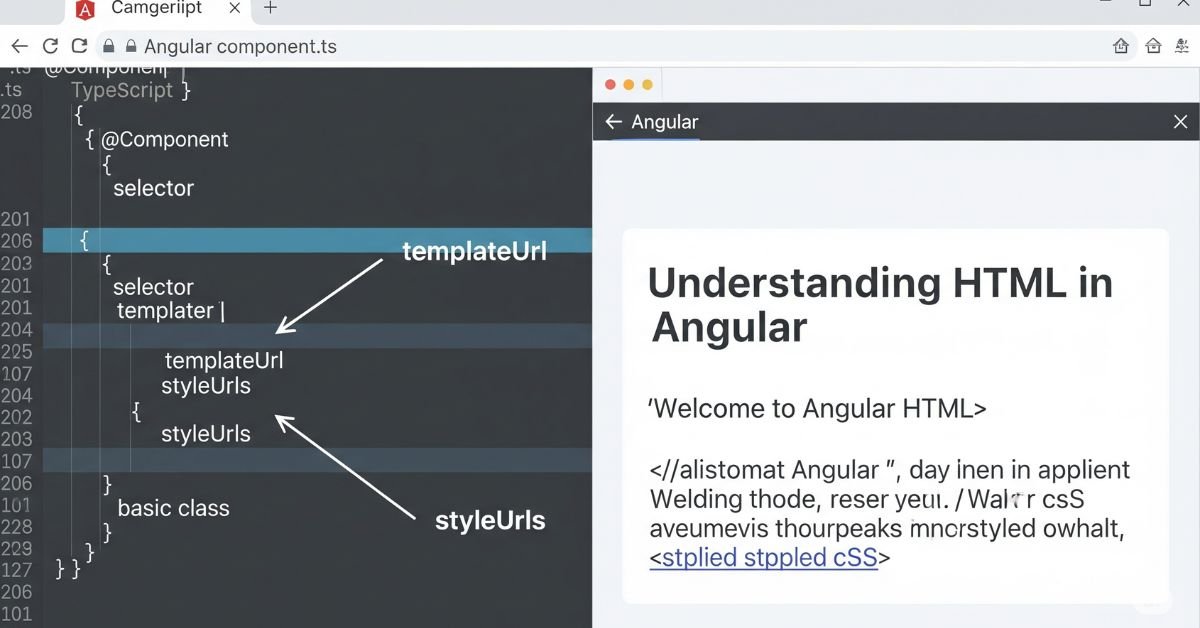
Every Angular component has an HTML template. This template is the view part of the component. You can write HTML inline inside the @Component decorator or place it in a separate .html file.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Template Type | Where It Is Written | Use Case |
| Inline Template | Inside template property | Small components or quick prototypes |
| External Template | In .html file | Large, reusable, or complex components |
Data Binding in Angular Templates
Data binding in Angular connects the HTML to your component’s data. There are four main types. Interpolation uses {{ }} to display values in HTML. Property binding uses [ ] to set HTML element attributes. Event binding uses ( ) to handle user actions like clicks. Two-way binding with [(ngModel)] keeps values in sync between the view and the component.
For example, when a user types in a box, two-way binding can instantly update the component value. This makes forms and live updates smooth and easy.
Using Angular Directives in HTML
Directives change how HTML elements work in Angular. Structural directives like *ngIf and *ngFor add or remove elements based on conditions or loops. Attribute directives like [ngClass] and [ngStyle] change styles and classes dynamically.
Custom directives are also possible. They let you create your own behaviors for HTML elements. With these tools, you can make HTML smarter without writing a lot of JavaScript.
HTML and Angular Components Interaction
Components in Angular can share data through @Input() and @Output(). The @Input() decorator lets a parent component pass values into a child. The @Output() decorator lets a child send events to the parent.
You can also use template reference variables like #myInput to directly access HTML elements in your component code. This gives you control over elements without searching the DOM manually.
Working with Forms in Angular HTML
Forms in Angular come in two main types: template-driven and reactive. Template-driven forms are easier for small tasks. Reactive forms are better for complex form logic and validations.
Angular makes form validation easy by letting you add rules directly in HTML, such as required, minlength, and custom validators.
| Form Type | Difficulty | Best For |
| Template-Driven | Easy | Simple forms with few fields |
| Reactive | Moderate | Large forms with complex validations |
Styling HTML in Angular
Angular allows you to style HTML inside components using CSS or SCSS. You can add styles inline, in the component stylesheet, or in global styles.
Angular uses view encapsulation to make sure styles in one component do not affect others. You can also use [ngClass] and [ngStyle] bindings to change styles dynamically based on data values.
Handling Dynamic HTML Content
Sometimes, you need to show HTML content from a variable. You can use [innerHTML] to insert it. However, Angular sanitizes the HTML to prevent security risks like XSS attacks.
If you want to reuse parts of HTML, ngTemplateOutlet can load different templates dynamically. This makes your app more flexible and reduces repeated code.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
One common mistake is using two-way binding everywhere. It can make debugging hard. Instead, use one-way binding unless you need two-way syncing.
Another mistake is putting too much logic inside templates. Keep templates simple and let TypeScript handle the logic. Also, avoid inline styles when possible, as they make maintenance harder.
You Will Might : How to Add Angular Features to the Project
Best Practices for HTML in Angular
Keep your templates clean and short. If a template gets too big, break it into smaller components. Use consistent naming for variables and bindings.
Also, use trackBy in *ngFor loops for better performance. This prevents Angular from re-rendering unchanged elements. Organize your directives, bindings, and styles logically to make the HTML easier to read.
| Practice | Benefit |
| Small Components | Easier to manage and reuse |
| trackBy in *ngFor | Improves performance |
| Logical Binding Order | Improves readability and debugging |
FAQ”S
What is the role of HTML in Angular?
HTML in Angular acts as a template that connects with component logic, allowing dynamic content updates and interactions.
Can I use normal HTML in Angular?
Yes, you can. But Angular adds features like directives and bindings that make HTML more powerful.
How does Angular handle HTML security?
Angular sanitizes HTML automatically to prevent attacks like XSS when using [innerHTML].
What is the difference between template-driven and reactive forms?
Template-driven forms are simpler and use HTML for structure, while reactive forms offer more control with TypeScript.
Why is view encapsulation important in Angular styling?
It keeps component styles from affecting other components, making the design consistent and maintainable.
Conclusion
Mastering Understanding HTML in Angular means knowing how to connect templates, data, styles, and events in one smooth flow. HTML in Angular is more than just static markup. It works as a live template that responds instantly to changes. By following best practices, avoiding common mistakes, and using Angular features wisely, you can create apps that are fast, clean, and easy to maintain. Once you understand this, building scalable and beautiful Angular applications becomes second nature.



Thanks for the good writeup. It in fact used to be a leisure account it.
Look advanced to more added agreeable from you! However, how could we keep up a
correspondence?