HTML is an acronym for hypertext Markup Language. It is technically not a programming language either. Essentially, it is how we instruct a browser to display stuff. HTML is combined with CSS and JavaScript. The design and colors are handled by CSS and the entertainment and motion are added by JavaScript. If you had no HTML, the other two would be pointless because there would be nothing on the webpage to design or to animate.
Think about HTML like the frame of a house. CSS is the paint and design. JavaScript is the electricity and moving parts. A beginner must always start with HTML because it gives the structure to everything else. That is why this HTML Tutorial for Beginners focuses on strong foundations first.
Setting Up Your Environment

Before you write your first HTML code you need a space to work. The most common tool is a code editor. Many people use Visual Studio Code because it is free and easy. Others use Sublime Text or even Notepad. The truth is you can write HTML in any plain text editor.
Once you have your editor, you also need a browser. Chrome, Firefox, and Edge all have built-in developer tools. These tools let you check your code, see errors, and test changes quickly. Save your first file as index.html. Double-click it and it will open in the browser. That simple step is the first victory for any beginner.
You will like this: Is Learning HTML and CSS Worth It in 2025?
Understanding HTML Document Structure

Every page begins with <!DOCTYPE html>. This tells the browser the document is HTML5. The next tag is <html>. Inside it there are two main parts: <head> and <body>.
The head contains information like the title, meta description, and links to CSS or scripts. The body holds everything a visitor can see like text, links, and images. When you understand this structure you can always find your way in any file.
Basic HTML Tags
The HTML Tutorial for Beginners must cover the basic tags. Headings go from <h1> to <h6>. They help organize text. Paragraphs use <p>. If you want a line break, you use <br>. To create a divider you use <hr>.
Comments are another key part. You write them with <!– comment here –>. They are not visible to users but help you remember what the code does. Beginners often skip comments but later find them very useful in big projects.
Formatting and Styling Text

HTML can also format words. You can make text bold with <b> or <strong>. The <strong> tag has extra meaning because it tells search engines the word is important. Italic is done with <i> or <em>. Again <em> adds meaning for emphasis.
You can underline text or even add superscript and subscript. These are useful in math or science content. The lesson here is simple. Use semantic tags whenever possible because they add value for both search engines and screen readers.
Read more: How Long Does It Take to Learn CSS Basics?
Links and Navigation
The internet is built on links. The <a> tag creates them. You must add href=”URL” inside the tag. A link can go to another site or another page within your own.
There are two types of paths. A relative URL points to a file inside your project. An absolute URL points to a full web address like https://example.com. If you want the link to open in a new tab, add target=”_blank”. Anchors can also link to a part of the same page using an id.
Working with Images

Images make a page come alive. The <img> tag adds them. You must use the src attribute to point to the file. The alt attribute is just as important because it describes the image. This helps users with screen readers and also helps SEO.
There are many image formats. JPG is common for photos. PNG supports transparent backgrounds. GIF is used for simple animations. SVG is scalable and great for icons. WebP is modern and small in size. Beginners should always compress images to make pages load faster.
Common Image Formats in HTML
| Format | Best Use Case | Notes |
| JPG | Photos | Small size, no transparency |
| PNG | Graphics | Supports transparency |
| GIF | Animations | Limited colors |
| SVG | Icons/Logos | Scales without loss |
| WebP | All images | Modern and efficient |
Creating Lists

HTML has three types of lists. Ordered lists <ol> use numbers. Unordered lists <ul> use dots. Description lists <dl> explain terms with definitions.
Lists can be nested inside each other. For example, you can have a numbered list with a nested bullet list. This is very useful for showing steps or organized information. Beginners often find lists helpful when creating menus or showing features.
Building Tables
Tables display data in rows and columns. The basic structure starts with <table>. Inside it you have rows <tr>. Each row contains cells which are either <td> for data or <th> for headings.
You can merge cells with colspan and rowspan. Captions can describe what the table is about. The best practice is to always use headers for accessibility. A table is not just for numbers but can also organize any type of data.
HTML Table Tags and Purpose
| Tag | Purpose | Example Use |
| <table> | Defines table | Holds all rows and cells |
| <tr> | Creates a row | Organizes cells in line |
| <td> | Adds data cell | Numbers, text, or links |
| <th> | Creates header cell | Column headings |
| <caption> | Describes the table | Title for data |
Forms and Input Elements
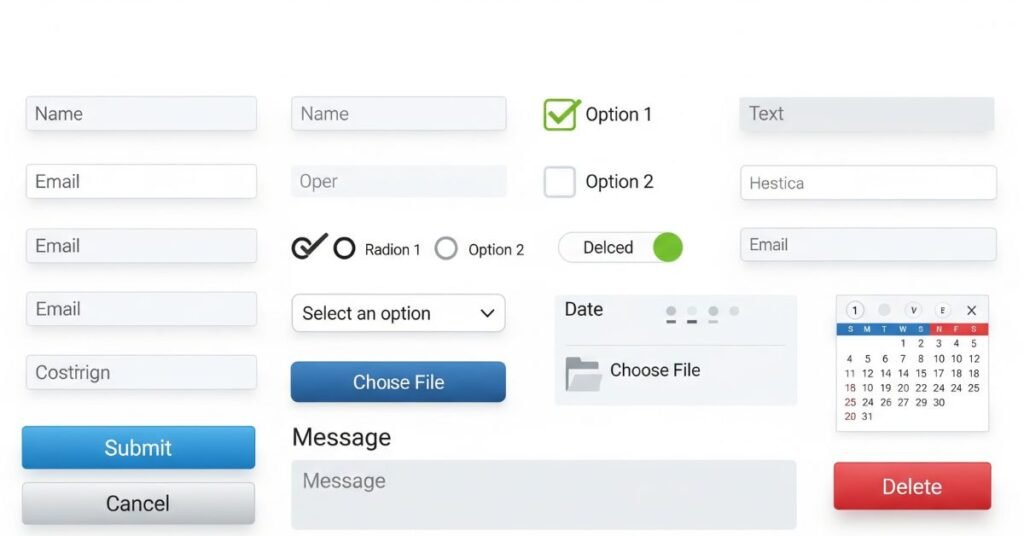
Forms collect user information. The <form> tag creates them. Inside you add input elements like text, email, password, checkbox, radio, and file upload.
Each input should have a <label> so users know what to enter
. A form needs an action attribute that tells the browser where to send the data. The method attribute is either GET or POST. Beginners should know GET shows data in the URL while POST hides it.
Introduction to Semantic HTML
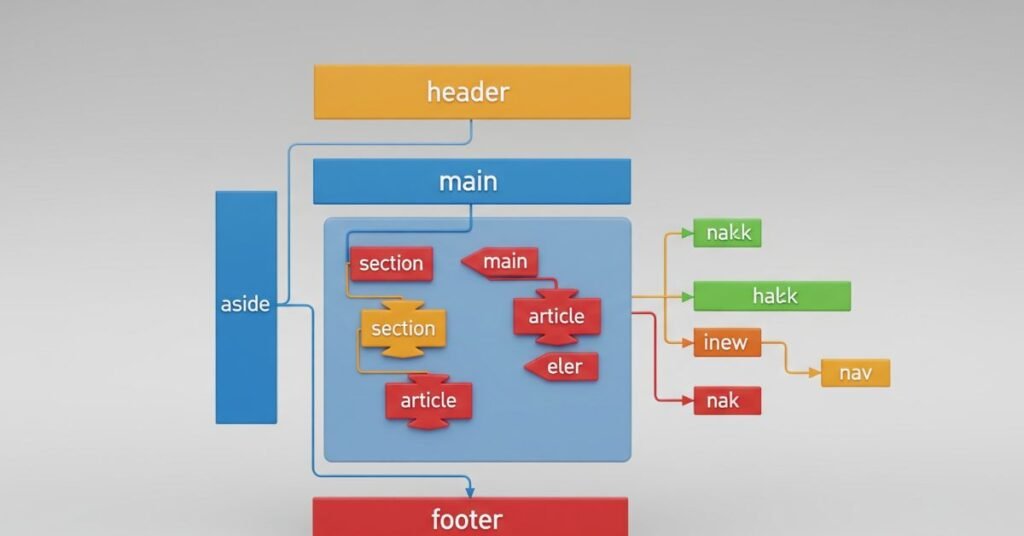
Semantic HTML means tags that carry meaning. For example <header> tells the browser it is the top section. <nav> means navigation links. <main> is the core content. <section> and <article> divide content logically. <footer> is the bottom part.
Search engines and screen readers use these tags to understand the page better. Using semantic tags improves SEO and accessibility. That is why every HTML Tutorial for Beginners must explain them clearly.
HTML Attributes and Best Practices

Attributes give extra information to tags. The most common are id, class, title, and lang. You can also use custom data attributes like data-price=”100″. These help JavaScript read hidden values.
Best practice is always to keep HTML clean. Indent your code. Use lowercase letters for tags. Add alt text for images. Do not use inline styles unless testing. For accessibility, use ARIA roles where needed. These small habits make your code easier to maintain.
Putting It All Together

Now it is time to build a small project. Create a webpage that has a heading, a paragraph, a link, and an image. Add a list of items. Insert a table with two columns and three rows. Finally create a form that asks for name and email.
When you open this file in a browser you will see a complete page. It may look simple but it shows everything you learned. That is the real power of HTML. Small steps add up to a working project.
Example Webpage Structure
| Element | Purpose | Example Code |
| Heading | Page title | <h1>Welcome</h1> |
| Image | Show a picture | <img src=”photo.jpg” alt=”sample”> |
| List | Display items | <ul><li>Item</li></ul> |
| Table | Organize data | <table><tr><td>Data</td></tr></table> |
| Form | Collect input | <form><input type=”text”></form> |
Next Steps After Learning HTML
Once you finish the HTML Tutorial for Beginners you should not stop. HTML is just the start. The next step is CSS. It lets you style colors, fonts, and layouts. After CSS comes JavaScript which adds dynamic features like slideshows and forms that check errors instantly.
You should also practice by building small projects. Make a portfolio page. Try a blog layout. Rebuild a simple site you like. The more you practice the stronger your skills become. Free resources like MDN Web Docs and W3Schools can guide you further.
FAQ’’S
Is HTML hard to learn for beginners?
No, HTML is easy. It uses simple tags and structures. Most people can build a page in one day.
Can I make a website using only HTML?
Yes, but it will look very plain. You need CSS and JavaScript to make it modern.
What is the difference between HTML and CSS?
HTML is for structure. CSS is for style. They always work together.
Which editor is best for learning HTML?
Visual Studio Code is popular. It is free and has many extensions.
How long does it take to master HTML?
You can learn basics in a week. To master it takes longer because you must practice and use it in real projects.
Conclusion
The HTML Tutorial for Beginners is your first door into the world of web development. You now know the structure of a page, the purpose of tags, and how to build a simple project. The skills you learned here are the same ones used by professional developers every day. Keep practicing and adding CSS and JavaScript to your learning path. Each page you build will make you better. Soon you will be able to create websites that look modern and work well for everyone.