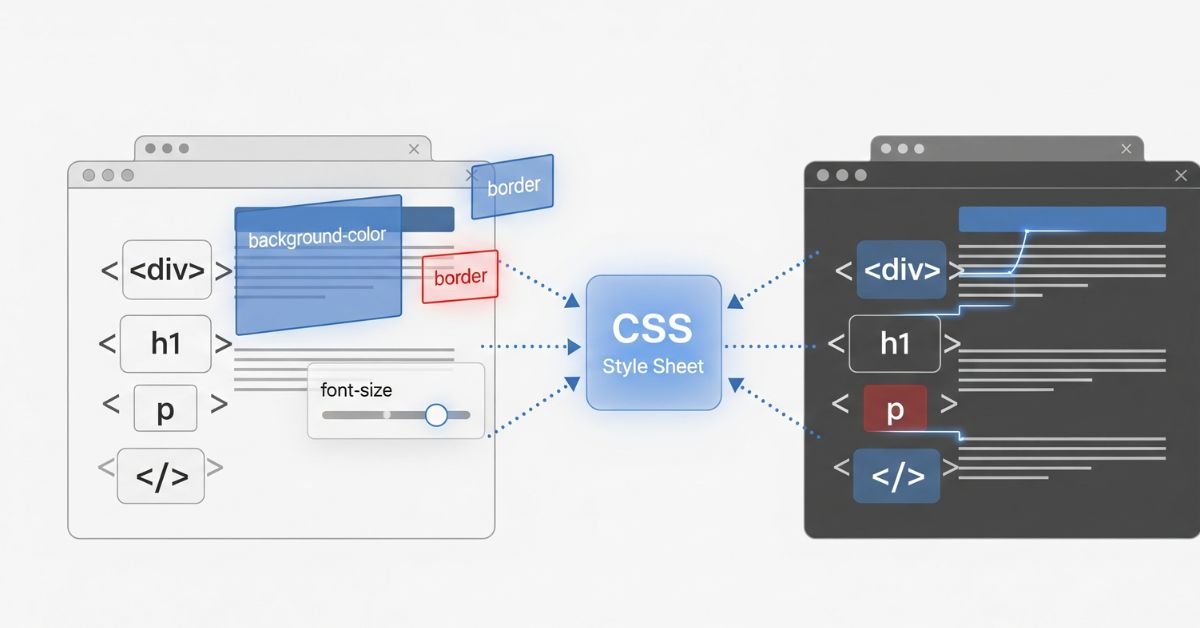
So, understanding how CSS works in web development is super crucial for every web developer out there. CSS, which stands for Cascading Style Sheets, is basically what makes websites look and feel awesome. Without it, all websites would just be boring with only the basic HTML structure. When you throw in some CSS, you’re adding color, layout, and design that really brings things to life. You can think of it like the clothes and vibe of a web page. In this guide, you’ll check out what role CSS plays, how it works, the different types, layout models, and the tools that help make modern sites smooth and responsive.
Role of CSS in Web Development
CSS gives structure meaning by adding style. HTML builds the skeleton of a site. CSS acts like the skin, clothes, and appearance. With it, you can define fonts, colors, and layout spacing. A site without CSS is like a house without paint or furniture.
Beyond style, CSS improves user experience. Consistent design makes a site easier to read and navigate. It also plays a big role in accessibility. For example, CSS allows resizing of text or adjusting colors for color-blind users. Businesses depend on it to build brands. The same CSS rules applied across pages create trust and identity.
You will like this: HTML Tutorial for Beginners
How CSS Works Under the Hood
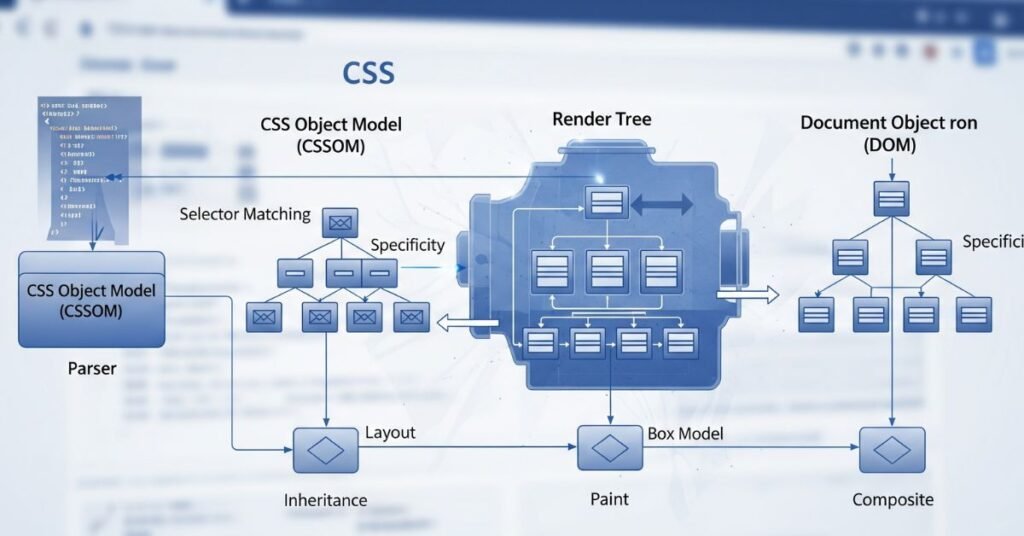
CSS works with rules made up of selectors, properties, and values. A selector picks the element, such as a paragraph or heading. The property defines what you want to change, like color or size. The value sets the detail. For example, p {color: red;} makes all text in paragraphs red.
The “cascade” decides which style wins when there is conflict. Order matters, as does specificity. An inline style beats an external stylesheet. Browser engines read CSS, build a render tree, and paint the page. This process happens in milliseconds, yet it decides exactly what you see.
Types of CSS and Their Usage
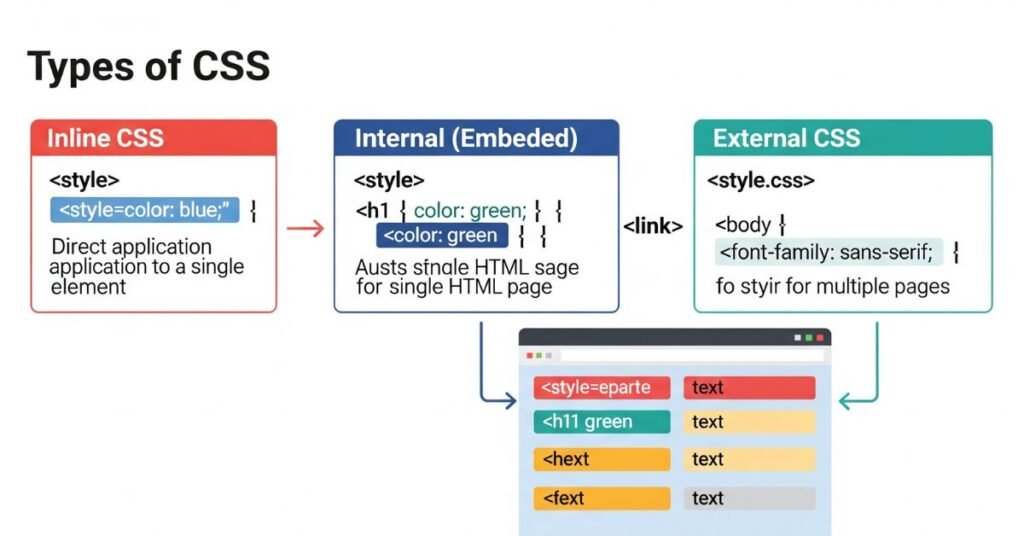
There are three main types: inline, internal, and external CSS. Inline styles go inside HTML tags. Internal CSS sits within the <style> tag in the HTML head. External CSS uses a separate .css file linked to HTML.
Inline CSS is quick but messy. Internal CSS works for small projects. External CSS is the standard for real websites. It keeps styles in one file, easy to update and reuse. Modern development almost always favors external stylesheets for maintainability.
CSS Box Model Explained
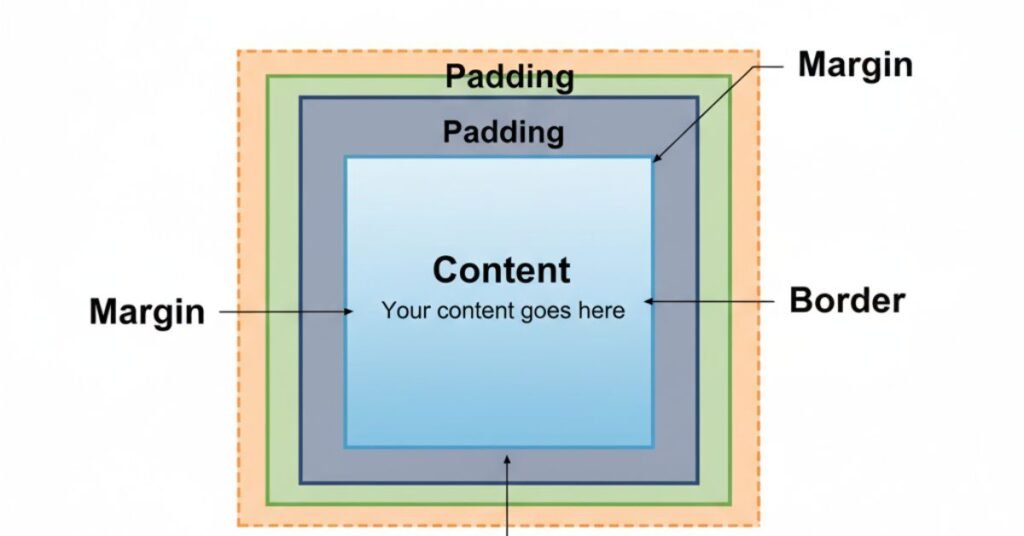
The CSS box model is the heart of layout. Every element on a web page is a rectangular box. This box has four layers: content, padding, border, and margin. Understanding these layers avoids layout disasters.
There are two models: content-box and border-box. Content-box is the default, where width means only the content. Border-box includes padding and border in the total width. Choosing the right model saves time. Many developers prefer border-box to avoid extra math when sizing.
| Layer | Meaning | Example Value |
| Content | Actual text or image | 200px width |
| Padding | Space between content and border | 20px |
| Border | Line surrounding padding | 2px solid |
| Margin | Space outside border | 15px |
Layout Techniques in CSS
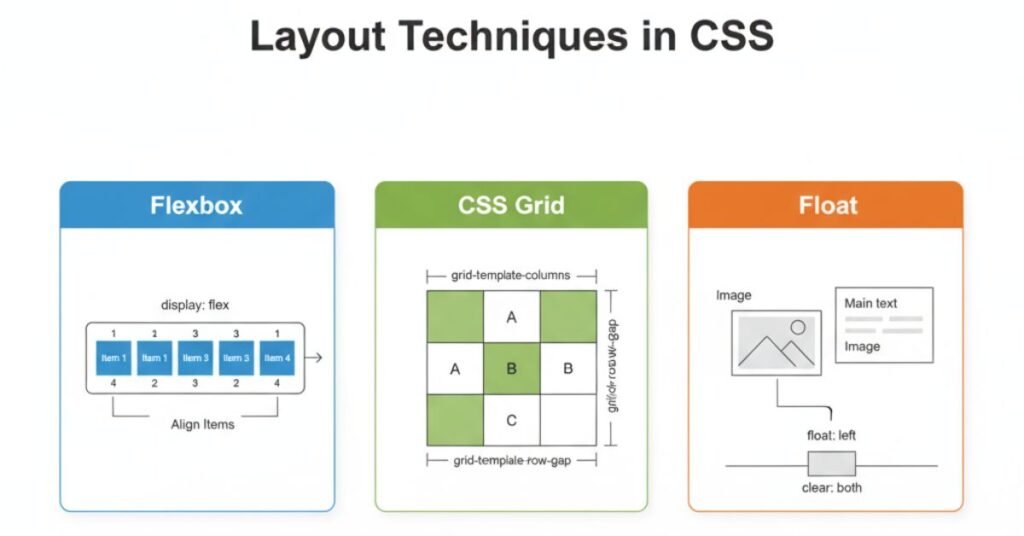
Early websites used floats for layout. This was never their true purpose, yet it became a hack. Today, floats are rare and replaced by better tools.
Modern CSS uses Flexbox and Grid. Flexbox works best for one-dimensional layouts, like a navigation bar. Grid is ideal for two-dimensional layouts, like full page templates. Positioning rules such as absolute, fixed, and sticky allow elements to move outside normal flow.
| Layout Method | Best For | Example Use |
| Floats | Legacy, wrapping text | Old blog layouts |
| Flexbox | One-dimensional alignment | Menus, toolbars |
| Grid | Two-dimensional layouts | Dashboards, web pages |
Responsive Design with CSS
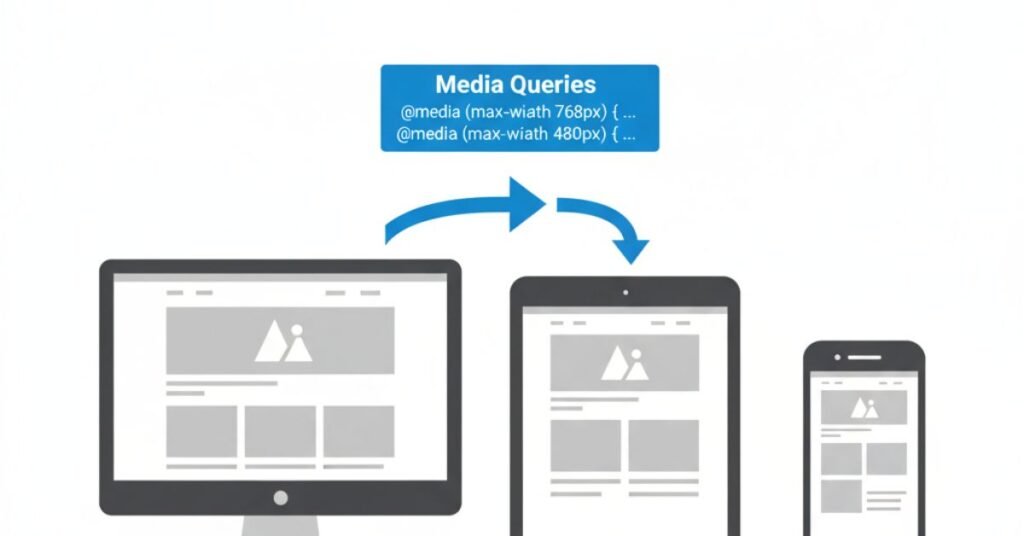
Responsive design makes sites adapt to screens. A desktop monitor, tablet, and smartphone all need different layouts. CSS makes this possible.
Media queries are the main tool. They check the device width and apply new styles. A mobile-first approach is now common. Start with a simple small screen layout, then expand for larger screens. New CSS features like clamp(), min(), max(), and container queries give even more control.
Read more: Difference Between HTML and CSS
Advanced CSS Features and Concepts

Modern CSS has grown beyond simple styling. Pseudo-classes like :hover or :focus change style based on user interaction. Pseudo-elements like before add content without editing HTML.
CSS also handles animations and transitions. You can fade elements, slide menus, or spin icons. CSS variables, also called custom properties, allow reusing values. New features such as subgrid and nesting make CSS even more powerful.
CSS Tools and Frameworks

Frameworks make CSS faster to use. Bootstrap offers ready-made components and a grid system. Tailwind CSS is utility-first, letting you style with small classes. Foundation is another powerful framework, though less common now.
Preprocessors like Sass and LESS add features like variables, nesting, and mixins. PostCSS and autoprefixers ensure compatibility with old browsers. These tools save time, but they can also bloat code. Developers must balance speed with performance.
| Tool/Framework | Key Feature | Pros | Cons |
| Bootstrap | Prebuilt components | Fast setup | Heavy codebase |
| Tailwind CSS | Utility classes | Customizable, lightweight | Steep learning curve |
| Sass | Nesting, variables | Cleaner, reusable code | Requires compiling |
CSS Best Practices for Developers

Good CSS is clean and structured. Naming systems like BEM (Block, Element, Modifier) or SMACSS help keep styles clear. They make it easier for teams to work on large projects.
Performance also matters. Too many complex selectors or unused styles slow down rendering. Developers should audit styles and remove waste. Browser dev tools can inspect, debug, and optimize. The key is writing CSS that is easy to read, maintain, and scale.
Future of CSS in Web Development

CSS continues to evolve. The W3C works on new standards like container queries and subgrid. These features solve long-standing layout issues. Developers can now experiment in modern browsers.
Frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular also use CSS in unique ways. CSS-in-JS, for example, scopes styles to components. The future shows CSS moving closer to full design systems. It will remain the essential skill for frontend developers.
CSS and Browser Compatibility

Not all browsers treat CSS the same way. A style that looks perfect in Chrome might break in Internet Explorer or an older version of Safari. This is why browser compatibility matters so much.
Modern tools like Autoprefixer help. They add missing vendor prefixes so new CSS works across browsers. Developers also use sites like Can I Use to check if a property is supported. Testing on multiple browsers and devices is still the safest way to avoid issues. A good site looks the same everywhere, from a big desktop screen to a small budget phone.
CSS and Web Performance

CSS affects not only how a site looks but also how fast it loads. Large, unused stylesheets slow down rendering. A browser must download, parse, and apply every line of CSS before showing the page.
Developers can improve performance by minifying CSS, removing unused styles, and loading only what’s needed. Inline critical CSS (styles needed for the first visible content) speeds up the first paint. Lazy-loading non-essential styles is another technique. Clean and optimized CSS helps users stay longer and improves SEO rankings.
Real-World Applications of CSS

CSS powers every modern website. Online stores use CSS grids and flexbox to display products in neat layouts. News websites rely on CSS typography to improve readability. Social media platforms use CSS animations and transitions to make interactions smooth.
Even apps built with frameworks like React or Vue still depend on CSS. Without it, the best JavaScript app would look unfinished. Whether it’s a blog, e-commerce site, or dashboard, CSS plays a central role in creating a professional and user-friendly design.
Learning and Mastering CSS

Learning CSS is a journey. At first, it feels simple. You change colors or add fonts, and the results appear instantly. But as projects grow, CSS becomes more complex. Layouts, responsiveness, and animations require deeper knowledge.
The best way to master CSS is practice. Start with small projects, like personal websites. Then move to larger ones where you handle grids, flexbox, and responsive design. Online resources like MDN Web Docs and free courses make learning easier. With time, you will not just style pages but design experiences. CSS is a skill that keeps rewarding you the more you learn.
FAQ’’S
What is CSS in simple words?
CSS means Cascading Style Sheets. It tells the browser how to style HTML.
Why is CSS important for web development?
CSS makes websites look good. It adds color, spacing, layout, and animations.
What are the three types of CSS?
Inline CSS, internal CSS, and external CSS. External CSS is best for large projects.
How does the CSS cascade work?
The cascade decides which style wins. Order, importance, and specificity matter.
What is the future of CSS?
New features like container queries and subgrid are coming. They will make CSS even more powerful.
Conclusion
How CSS Works in Web Development shows the power behind website design. It controls layout, colors, and responsiveness. From the box model to frameworks, CSS drives the look of the web. Mastering CSS means more than knowing rules. It means creating clean, fast, and beautiful sites. Developers who stay updated will shape the web of tomorrow.