The Difference Between HTML and CSS is one of the first lessons you’ll face when learning web development. HTML and CSS are the foundation of every website. You can imagine HTML as the bricks of a house and CSS as the paint, furniture, and decoration that make it look alive. A page with only HTML works, but it looks plain. A page with only CSS cannot even exist because CSS needs HTML to apply its design. This is why learning the difference between HTML and CSS is vital for beginners who want to create websites that are both functional and beautiful.
What is HTML?

HTML means HyperText Markup Language. It is the language used to structure a webpage. Think of it as the skeleton that holds everything in place. With HTML you add text, images, tables, headings, and links. Every article you read online, every product page you see in a store, and every video you click starts with HTML.
HTML is not a programming language. Instead, it is a markup system that uses elements to describe how content should appear. For example, a headline, a paragraph, and a picture all use different elements. These elements tell the browser what kind of content it is showing. Without HTML, the internet would be empty.
You will like this: HTML Tutorial for Beginners
What is CSS?

CSS means Cascading Style Sheets. It is the language that controls the look of a webpage. While HTML builds the body, CSS decides the outfit. CSS changes colors, fonts, spacing, alignment, and layout. If HTML is the skeleton, CSS is the skin and style that makes it appealing.
CSS also makes pages responsive, meaning they adapt to different screens like phones, tablets, and desktops. Without CSS, every website would look like plain black text on a white background. It is CSS that makes modern websites attractive and easy to use. Designers and developers rely on CSS to control everything from button colors to multi-column layouts.
Key Differences Between HTML and CSS

The Difference Between HTML and CSS comes down to purpose. HTML gives structure, CSS gives style. HTML works with elements, CSS works with rules. HTML alone can create content, but CSS alone is useless without HTML. Another difference is that HTML is easier for beginners, while CSS takes more practice to master.
Here’s a simple table to make the differences clearer:
| Feature | HTML | CSS |
| Purpose | Structure and content | Style and layout |
| Language type | Markup language | Style sheet language |
| Example use | Adding text, links, images | Changing colors, spacing, fonts |
| File extension | .html | .css |
| Difficulty | Very beginner-friendly | Easy at first but harder for advanced designs |
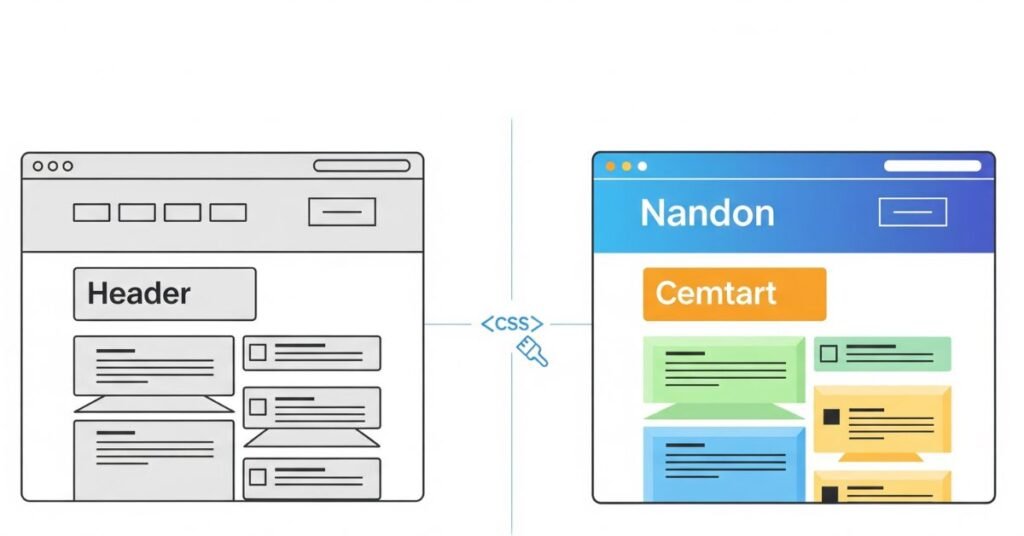
How HTML and CSS Work Together

HTML and CSS are like teammates. HTML provides the text, headings, and images, while CSS decides how they look on the screen. Without HTML, CSS has no content to design. Without CSS, HTML looks plain and unstyled. They must work together to form a complete website.
There are different ways to connect CSS with HTML. The most common way is using a separate CSS file. This method keeps everything organized. It also makes changes easier because you can update the style for hundreds of pages from one single file. This separation between content and style is what makes modern web design clean and efficient.
Read more: Is Learning HTML and CSS Worth It in 2025?
Why You Need Both HTML and CSS in Web Development

You can’t build a modern website with just one of them. HTML brings the actual content, like articles, forms, or product details. CSS makes sure people enjoy reading and navigating that content. Imagine reading a magazine with no layout, no pictures, no bold fonts—just plain words. That’s how a web page feels without CSS.
In addition, both HTML and CSS are the base for advanced tools like frameworks and content management systems. Bootstrap, Tailwind, WordPress, and even React all rely on HTML and CSS. Without knowing these basics, you’ll always struggle when working with higher-level tools.
Practical Examples and Use Cases
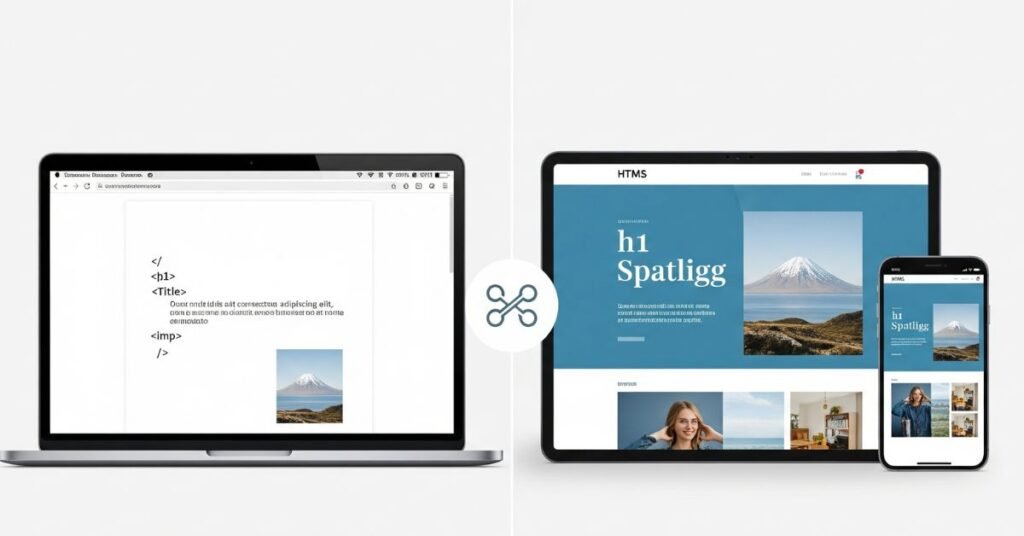
Think about two versions of a blog page. The first one uses only HTML. It has headlines, text, and images, but it looks dull and old. The second version uses both HTML and CSS. Now the text has proper spacing, colors match the theme, and the design feels inviting. This before-and-after effect shows the real difference between HTML and CSS in action.
Here’s a quick table to summarize:
| Website Version | Appearance | User Experience |
| HTML only | Plain, black and white | Hard to read, not attractive |
| HTML with CSS | Styled with colors and layout | Engaging, professional, user-friendly |
Common Mistakes Beginners Make

When learning the difference between HTML and CSS, beginners often mix their roles. Some try to style content with old HTML tags like <font>, which is outdated. Others use inline CSS everywhere, making their code messy and hard to maintain. Many forget about semantic HTML, which helps search engines and improves accessibility.
Here’s a useful table showing common mistakes and better practices:
| Mistake | Why It’s Wrong | Better Practice |
| Using old <font> tags | Outdated and not supported | Use CSS font properties |
| Mixing structure and design | Makes code messy | Keep HTML for content and CSS for style |
| Ignoring semantic HTML | Hurts SEO and accessibility | Use correct tags like header and footer |
| Overusing inline styles | Hard to manage large sites | Use external CSS files |
How HTML and CSS Affect SEO

When you think about the Difference Between HTML and CSS, it’s also important to see how both impact search engines. HTML is critical for SEO because it gives search engines the structure they need to understand a page. Headings, titles, meta descriptions, and alt text for images all come from HTML. If HTML is not well-structured, search engines might not index your page correctly.
CSS, on the other hand, influences SEO indirectly. A well-styled page loads faster and looks better, which keeps visitors engaged longer. If your site is hard to read or messy, people leave quickly, and this hurts your ranking. Google has made it clear that user experience is a ranking factor. A clean mix of HTML for structure and CSS for design creates pages that are both search-friendly and user-friendly.
How HTML and CSS Shape User Experience
User experience is one of the strongest reasons to learn both HTML and CSS. HTML provides accessibility features like proper tags for navigation and screen readers. If someone uses a voice assistant or a screen reader, semantic HTML ensures they can still interact with your site. Without this, large groups of users are excluded.
CSS makes sure users feel comfortable staying on the page. It controls font size, colors, and spacing. Think of reading a novel with tiny gray text on a black background—it would be exhausting. That’s what bad CSS does. Good CSS makes the design readable, responsive, and visually balanced. The difference between HTML and CSS directly shapes how people feel when visiting your site.
Real-Life Example
A blog and an e-commerce site both rely on HTML and CSS but in different ways. A blog needs HTML to create articles, headings, and images. CSS is used to style the text, make it readable, and ensure the layout adapts to mobile screens. Without CSS, a blog post would look like a wall of plain text.
An e-commerce site is more complex. HTML provides the product descriptions, pricing, and images. CSS adds the product grid, colors for sale items, and a responsive checkout page. Without CSS, you could still list products, but the site would not look professional or trustworthy. In business, poor CSS can cost sales. This shows why both languages are essential in practice.
The Future of HTML and CSS
Some beginners ask if HTML and CSS will ever become outdated. The answer is no. New technologies come and go, but HTML and CSS remain the backbone of the web. HTML5 introduced modern elements like video, audio, and semantic tags. CSS3 brought animations, flexbox, and grid systems. These updates show how the languages evolve with time.
In 2025 and beyond, HTML and CSS will continue growing. Developers are now using CSS for advanced animations and even 3D effects. HTML keeps expanding with new semantic elements that improve accessibility and SEO. Anyone learning web development must first master these two. Their difference will always be essential knowledge no matter how advanced web design becomes.
FAQ’’S
What is the main difference between HTML and CSS?
HTML is for structure and content, while CSS is for design and style.
Can a website work without CSS?
Yes, but it will look plain and unattractive. CSS makes it readable and engaging.
Is HTML easier to learn than CSS?
Yes. HTML is simpler, while CSS needs more practice for advanced layouts.
Do I need both HTML and CSS to build a website?
Yes. Without HTML, you have no content. Without CSS, you have no design.
Which should I learn first, HTML or CSS?
Learn HTML first, because you need structure before you can apply design with CSS.
Conclusion
The Difference Between HTML and CSS is simple but vital. HTML gives a site its structure, while CSS makes it look good. You need both to create a modern, professional, and user-friendly website. HTML builds the foundation, CSS adds the style, and together they create the internet as we know it. Without understanding both, your skills will always feel incomplete. Mastering the difference between HTML and CSS is the first step toward becoming a skilled web developer.